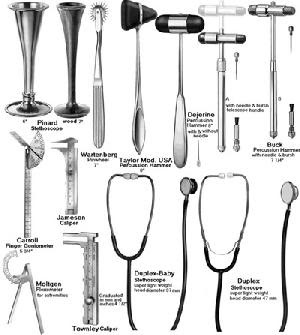
The stethoscope (from Greek στηθοσκόπιο, of στήθος, stéthos - chest and σκοπή, skopé - examination) is an acoustic medical device for auscultation, or listening to the internal sounds of an animal body. It is often used to listen to lung and heart sounds. It is also used to listen to intestines and blood flow in arteries and veins. In combination with a sphygmomanometer, it is commonly used for measurements of blood pressure. Less commonly, "mechanic's stethoscopes" are used to listen to internal sounds made by machines, such as diagnosing a malfunctioning automobile engine by listening to the sounds of its internal parts. Stethoscopes can also be used to check scientific vacuum chambers for leaks, and for various other small-scale acoustic monitoring tasks. A stethoscope that intensifies auscultatory sounds is called phonendoscope.
Saturday, August 13, 2011
Stethoscope
Labels:
Stethoscope
Stethoscope
Labels:
Stethoscope
Stethoscope
Labels:
Stethoscope
Stethoscope
Labels:
Stethoscope
Friday, August 12, 2011
ICU Monitor
A medical monitor or physiological monitor or display, is an electronic medical device that measures a patient's vital signs and displays the data so obtained, which may or may not be transmitted on a monitoring network. Physiological data are displayed continuously on a CRT or LCD screen as data channels along the time axis, They may be accompanied by numerical readouts of computed parameters on the original data, such as maximum, minimum and average values, pulse and respiratory frequencies, and so on.
In critical care units of hospitals, bedside units allow continuous monitoring of a patient, with medical staff being continuously informed of the changes in general condition of a patient. Some monitors can even warn of pending fatal cardiac conditions before visible signs are noticeable to clinical staff, such as atrial fibrillation or premature ventricular contraction (PVC).
In critical care units of hospitals, bedside units allow continuous monitoring of a patient, with medical staff being continuously informed of the changes in general condition of a patient. Some monitors can even warn of pending fatal cardiac conditions before visible signs are noticeable to clinical staff, such as atrial fibrillation or premature ventricular contraction (PVC).
Labels:
ICU Monitor
ICU Monitor
Labels:
ICU Monitor
ICU Monitor
Labels:
ICU Monitor
ICU Monitor
Labels:
ICU Monitor
Thursday, August 11, 2011
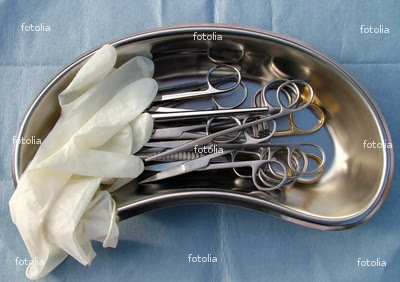
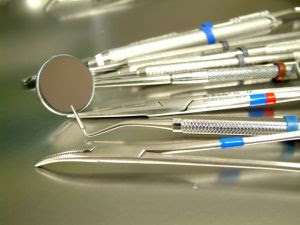
Doctors Instruments
Labels:
Doctors Instruments
Doctors Instruments
Labels:
Doctors Instruments
Doctors Instruments
Labels:
Doctors Instruments
Doctors Instruments
Labels:
Doctors Instruments
Tuesday, August 2, 2011
Blood Sugar Checking Machine
A glucose meter (or glucometer) is a medical device for determining the approximate concentration of glucose in the blood. It is a key element of home blood glucose monitoring (HBGM) by people with diabetes mellitus or hypoglycemia. A small drop of blood, obtained by pricking the skin with a lancet, is placed on a disposable test strip that the meter reads and uses to calculate the blood glucose level. The meter then displays the level in mg/dl or mmol/l.
Since approximately 1980, a primary goal of the management of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus has been achieving closer-to-normal levels of glucose in the blood for as much of the time as possible, guided by HBGM several times a day. The benefits include a reduction in the occurrence rate and severity of long-term complications from hyperglycemia as well as a reduction in the short-term, potentially life-threatening complications of hypoglycemia.
Since approximately 1980, a primary goal of the management of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus has been achieving closer-to-normal levels of glucose in the blood for as much of the time as possible, guided by HBGM several times a day. The benefits include a reduction in the occurrence rate and severity of long-term complications from hyperglycemia as well as a reduction in the short-term, potentially life-threatening complications of hypoglycemia.
Labels:
Blood Sugar Checking Machine
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)